Each year, more and more men are facing a general disease - prostatitis.Until recently, this problem was thought to occur only in elderly people, but in recent decades, the number of many young men who have signs of inflammatory prostate lesion has increased significantly.We will try to understand what the disease is, what are its symptoms, methods of diagnosis, methods of effective treatment.
What is prostatitis?
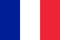
Prostatitis - a disease of the prostate or prostate gland - a very common disease of the male geniturine system.The reasons for it can be both infectious nature and caused by other factors.For example, weakening immunity, hypothermia, sedentary lifestyle, irregular or overly sexual life, nervous overloads, various infections, drinking alcohol, spices and fatty foods.
The prostate gland - one of the organs of the reproductive system in men - has a nut size and is at the beginning of the urethra.Its function is the development of a secret that is responsible for the viability of semen.
As a rule, four types of prostatitis are distinguished: acute, chronic abacus, chronic bacterial and asymptomatic chronic.The first type is the most rare and severe inflammation of the prostate gland, which occurs due to infection.It has pronounced symptoms: fever, fever, acute pelvic pain, blood in the urine, painful ejaculation and others.When identifying the disease, emergency medical care is required, often hospitalization.
The other forms are chronic and more pronounced symptoms, but more frequent and more difficult to diagnose.The signs of chronic prostatitis are: lower abdominal and back pain, disyuria, sexual disorders, purulent or transparent discharge from the urethra.With the asymptomatic course of the disease, there may be no noticeable manifestations and the diagnosis is only possible according to the results of the tests.
The prostatitis in men is generally found after 25 years, and representatives of the "strong half", which have reached 30-35 years, are most at risk.The risk of illness increases every decade.After forty -five, according to statistics, the disease is exposed to almost 50% of the male, therefore at this age it is recommended to be examined regularly to detect prostatitis at an early stage.
Diagnostics
When you contact a medical institution, the first thing you need to do is examine a urologist who can diagnose the disease or prescribe additional studies.The following diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the presence of prostate inflammation:
- A physical examination that involves palpation of the gland by a doctor to determine its size and condition;
- Transrectal ultrasound prostate examination - in other words, an ultrasound performed by a special sensor through the rectum;
- Study of the secret of the prostate, spread from the urethra on the leukocytes and the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the microflora;
- Ejaculate examination;
- General urine analysis - first, for leukocytes, protein and bacteria contained;
- Cytological and bacteriological examination of urine;
- Identification of the dog level - a special protein made from prostate cells;
- Urodynamic examination - in difficult cases, for a more accurate diagnosis;
- Cystoscopy - is used according to strict indications, mainly for injuries and before surgery.
The need to use specific diagnostic methods is determined by a doctor and the list can significantly reduce or, conversely, increase.Most importantly, it is accurate and timely to identify the presence of the disease and determine how to cure prostatitis.
Methods for treating prostatitis
Modern methods of treating prostatitis in men are very varied and depend on the degree and type of disease, the presence of complications, its prescription and the characteristics of the patient's body.
The procedures are performed on an outpatient basis in the hospital - the method depends on the specific situation, the well -being of the patient.You should contact a specialized urologist and preferably at the clinic, where you can first diagnose and take the necessary tests, and then, according to the results, you will be prescribed the appropriate course.It must be remembered that the disease can only be defeated with an integrated approach to treatment, it is impossible to ignore any advice of the doctor.
Drug therapy
Treatment of prostatitis drugs includes: taking antibiotics, ineffective drugs and alpha blockers.Antibiotics are mainly used as a method of treating bacterial prostatitis.Most often, doctors prescribe medicines that have existing substances such as ciprofloxacin, penicillin.Alpha-blockers are prescribed in chronic cases of the disease as an anesthetic and eliminating prostate edema, non-steroidal agents are used for acute forms of inflammation.
Remark
It is important to remember that medicines should only be prescribed by a urologist, an independent choice of medicines and suicide not only cannot alleviate the condition, but also worsen the course of the disease.
Surgery
Surgical manipulations for the treatment of prostatitis have been prescribed for a long time, but they have mixed results, so recently the popularity of radical methods is not so high.
Transurethral Prostate Resection (Tour)
It consists of removing part of the prostate or whole prostate tissue completely to weaken the pressure on the urethra.The result of the surgery is to get rid of the symptoms of inflammation - pain.It is produced in the so -called "closed" way - using a special apparatus that reduces the risk of complications.
Prostatectomy
"Open" intervention is the method of removing the gland using ordinary surgical instruments.It has a longer rehabilitation period than the circumference, but in some cases it is the only possible method.Leads to complete impotence of the patient.
Methods of non -surgical treatments
In recent years, minimally invasive methods for treating prostatitis in men have gained great popularity - as the most effective and at the same time they are not too painful.
- Thermal methods, the most common of them is microwave thermotherapy.Prostate reduction is achieved through the effects of high temperatures.
- Ultrasound- One of the most effective methods of therapy.It consists of the effects of ultrasound waves directly on the prostate gland.The advantages of this technique are not only with positive treatment results, but also in the convenience and lack of pain for the patient.
- CobbledThis implies the removal of inflamed tissue with the help of liquid nitrogen.
- Laser methodsThey show for the treatment of chronic prostatitis.When used, coagulation and evaporation of water from the prostate tissue occur.Also, the laser effect increases the body's protective functions and promotes tissue renewal.
- Magnetic laser induction therapy- This is a complex effect of a magnet and laser, which has a beneficial effect on blood circulation, helps to accelerate the healing process of damaged tissues, has an analgesic effect.In addition, this method increases the effect of medicines.
- Tied urethral dilationSWhen using this method, mechanical expansion of the urethra by introducing a special spray catheter at the end that is inflated.
- StentingProstate urethra also involves the expansion of the walls of the urethra, but already by introducing a stent - a cylindrical frame of polymer materials.It can be assigned in combination with the previous method.
- MassageIt is prescribed with other treatments and can significantly improve their effect.
- Methods of traditional Chinese medicine, more special, reflex therapy is the effect on the biologically active points of the patient's body with needles, heat and other physical factors.The proven effect of reflexology is to restore the balance of the endocrine system, improve the central nervous system, normalize blood flow and metabolic processes, elimination of neuralgic pain and inflammatory processes.Like the massage, you can use in combination with other methods.
As you know, men are often careless to their health and especially avoid visiting a clinic with such a strict problem as urological diseases.However, it is better to consult a doctor and get rid of the disease in the early stages than to deal with its consequences later.